Scalable Synthesis of Degradable Copolymers Containing α-Lipoic Acid via Miniemulsion Polymerization
Parker T. Morris, Kodai Watanabe, Kaitlin R. Albanese, Greggory T. Kent, Rohini Gupta, Matthias Gerst, Javier Read de Alaniz, Craig J. Hawker, Christopher M. Bates
J. Am. Chem. Soc. Oct. 2024
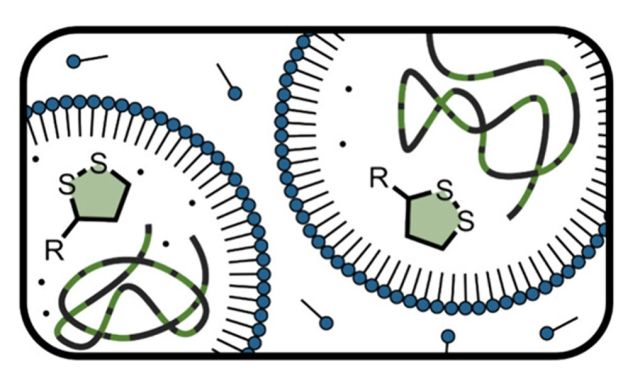
Abstract: A robust method is described to synthesize degradable copolymers under aqueous miniemulsion conditions using α-lipoic acid as a cheap and scalable building block. Simple formulations of α-lipoic acid (up to 10 mol %), n-butyl acrylate, a surfactant, and a costabilizer generate stable micelles in water with particle sizes <200 nm. The ready availability of these starting materials facilitated performing polymerization reactions at large scales (4 L), yielding 600 g of poly(n-butyl acrylate-stat-α-lipoic acid) latexes that degrade under reducing conditions (250 kg mol–1 → 20 kg mol–1). Substitution of α-lipoic acid with ethyl lipoate further improves the solubility of dithiolane derivatives in n-butyl acrylate, resulting in copolymers that degrade to even lower molecular weights after polymerization and reduction. In summary, this convenient and scalable strategy provides access to large quantities of degradable copolymers and particles using cheap and commercially available starting materials.